Reasons to Consider NIPS
Screening and diagnosis are different medical concepts. Screening uses simpler, safer, and less expensive methods and seeks to identify people who are at higher risk of some disease. (Note that expense can be defined in terms of money, human resources, effect on society, or time.) Conversely, diagnosis seeks to identify the precise health problem that is affecting a given person.
Methods exist to both screen for and diagnose Down syndrome. For example, blood serum screening during the 1st and 2nd trimester cannot determine whether the baby has Down syndrome with certainty. Rather, blood serum screening determines the probability that the baby suffers from Down syndrome according to maternal age, biochemical markers in the mother's blood, and ultrasound results. Further testing with alternative methods is recommended if the probability of Down syndrome is found to be high.
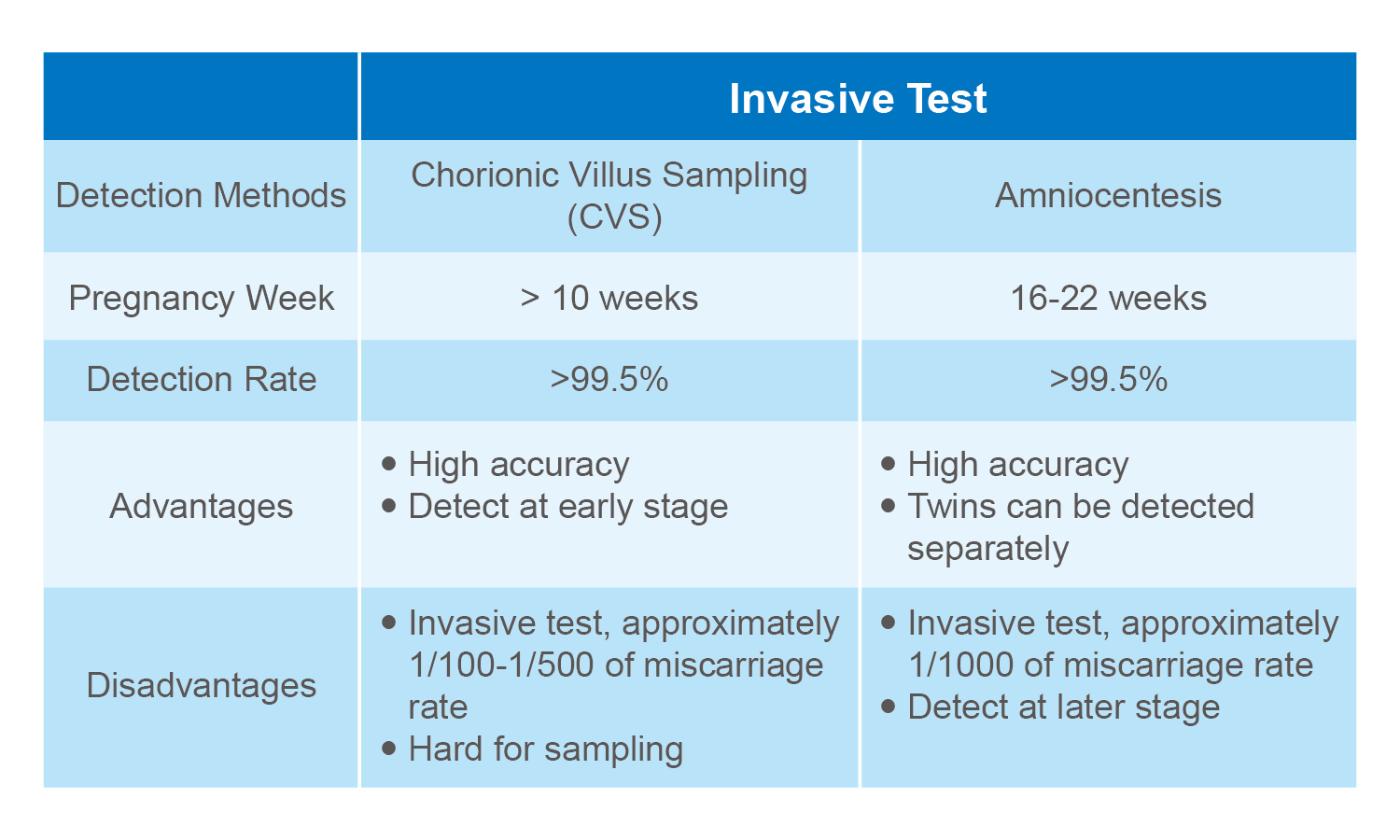
Amniocentesis is considered invasive due to the high medical risk and considerable financial expense associated with the procedure. Specifically, amniocentesis involves inserting a large needle into the uterus, which can cause infection, hemorrhage, uterine dysfunction, or leakage of amniotic fluid. Furthermore, around 1-3 pregnancies out of every 1000 end in miscarriage following amniocentesis. For a thirty year old mother, the chance of giving birth to a Down syndrome baby is around 1 in 800; however, the chance that amniocentesis leads to miscarriage is around 1 in 270. Therefore mothers are only recommended to undergo if the risk of Down syndrome is greater than 1 in 270 or if they are older than 34 years old (in other words, when the benefits of this procedure outweigh the risks).
Successfully performing amniocentesis requires a high level of skill. Indeed, the procedure is very risky even when performed by a doctor who has received comprehensive training. Currently, around 200,000 amniocentesis tests are requested each year, and it is impossible for obstetricians to meet this demand.
NIPS is a safe, accurate (detectability rate typically exceeds 99.5%), and highly feasible procedure. With just a small amount of maternal blood, parents can receive a complete evaluation of their baby.