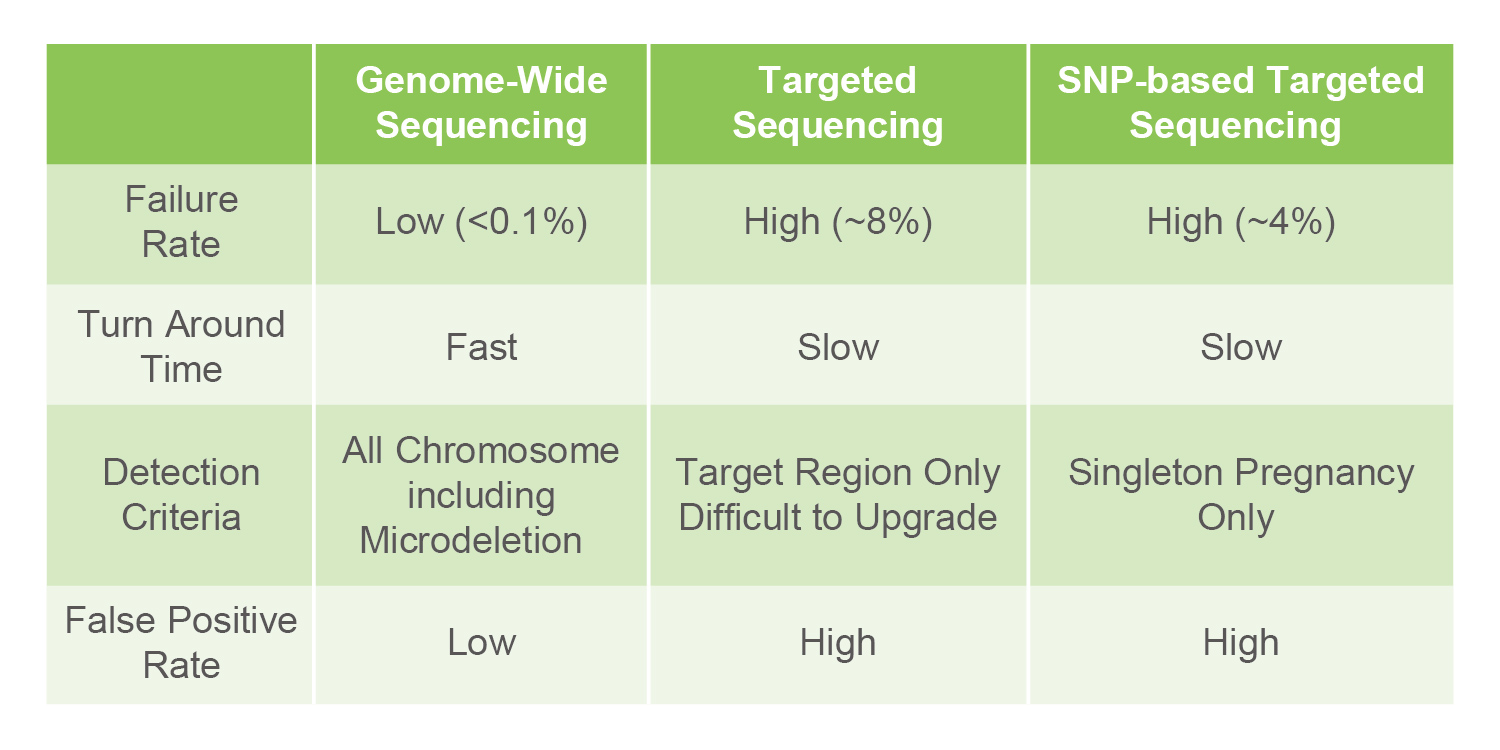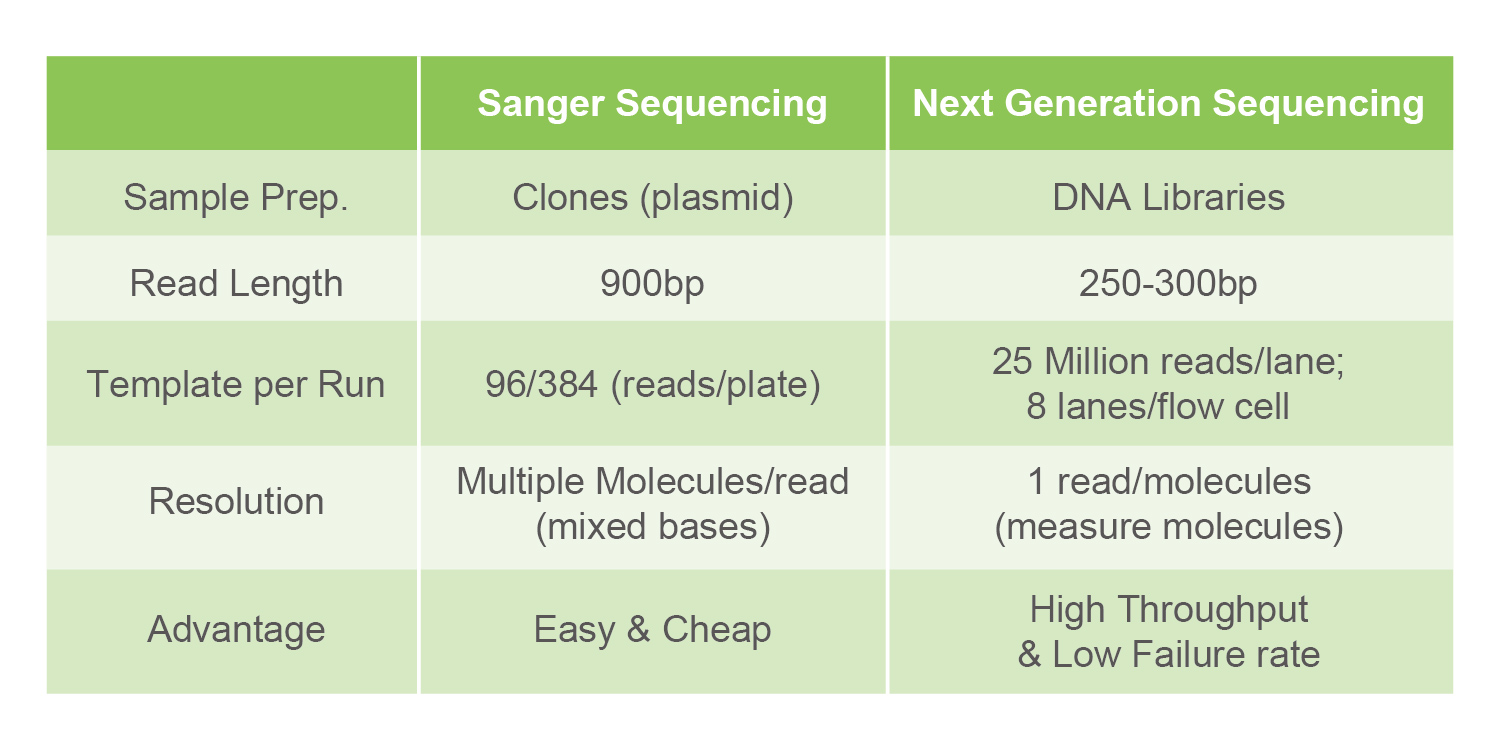
Several methods can be used to retrieve fetal DNA from the mother's blood: Genome-Wide Sequencing, Targeted Sequencing, and SNP based Targeted Sequencing.
Genome-Wide Sequencing is performed on the complete set of genes. Conversely, targeted Sequencing only targets those sequences which have a higher chance of being associated with abnormalities such as Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Patau syndrome, or Turner syndrome. SNP based Targeted Sequencing is able to ensure that the mother's genetic material does not confound test results. However, Genome-Wide Sequencing is currently more popular than other sequencing methods thanks to advances in technology, the ability to provide comprehensive results, as well as a fast speed and high success rate.