genome wide sequencing
Currently, there are three primary methods of performing NIPS: Genome-Wide Sequencing, Targeted Sequencing, and SNP based Targeted Sequencing. Genome-Wide Sequencing works is performed on the complete set of genes. Conversely, Targeted Sequencing only targets those sequences which have a higher chance of being associated with abnormalities, for example, on the 13th , 18th, and 21st chromosomes. Finally, SNP based Targeted Sequencing eliminates maternal DNA to obtain a purer fetal DNA sample.
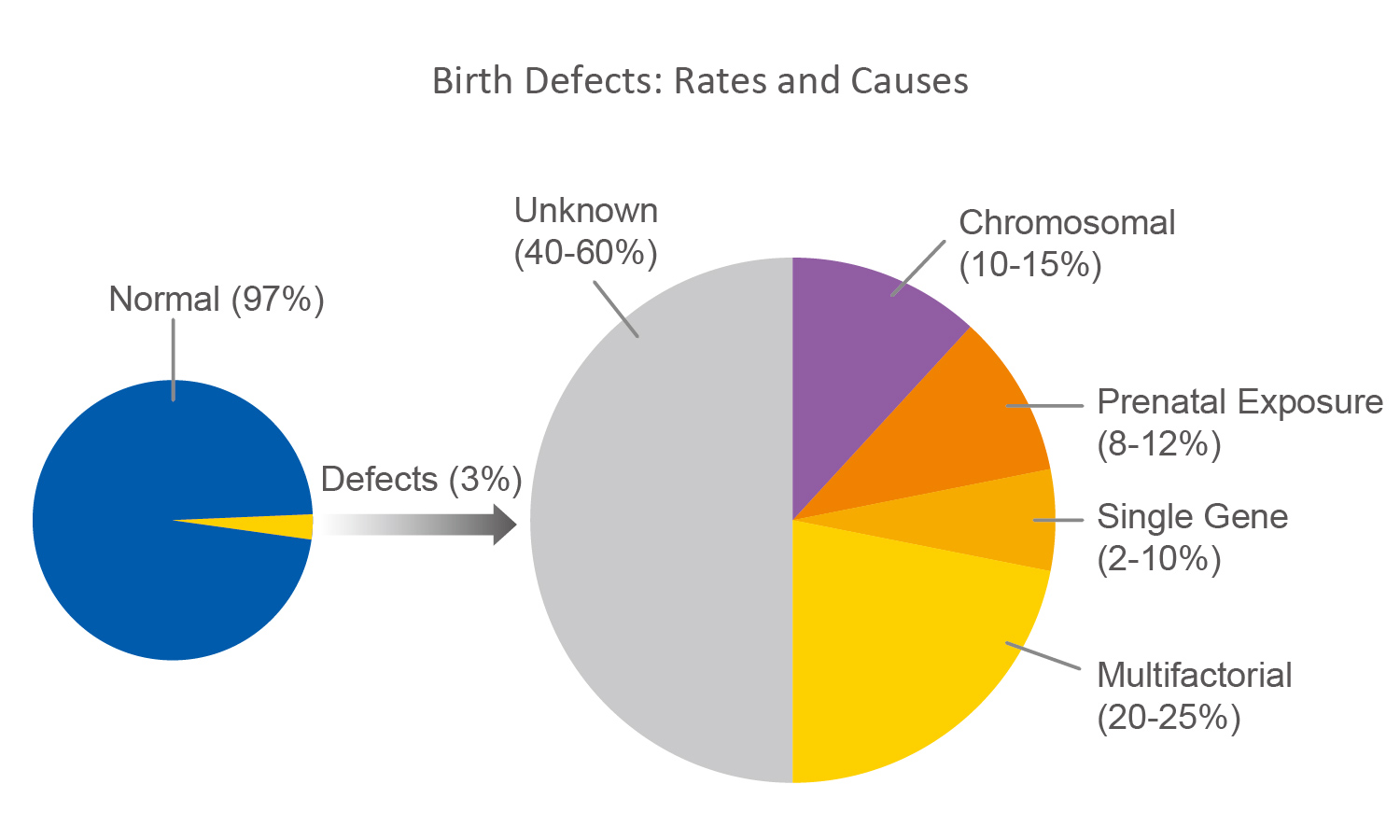
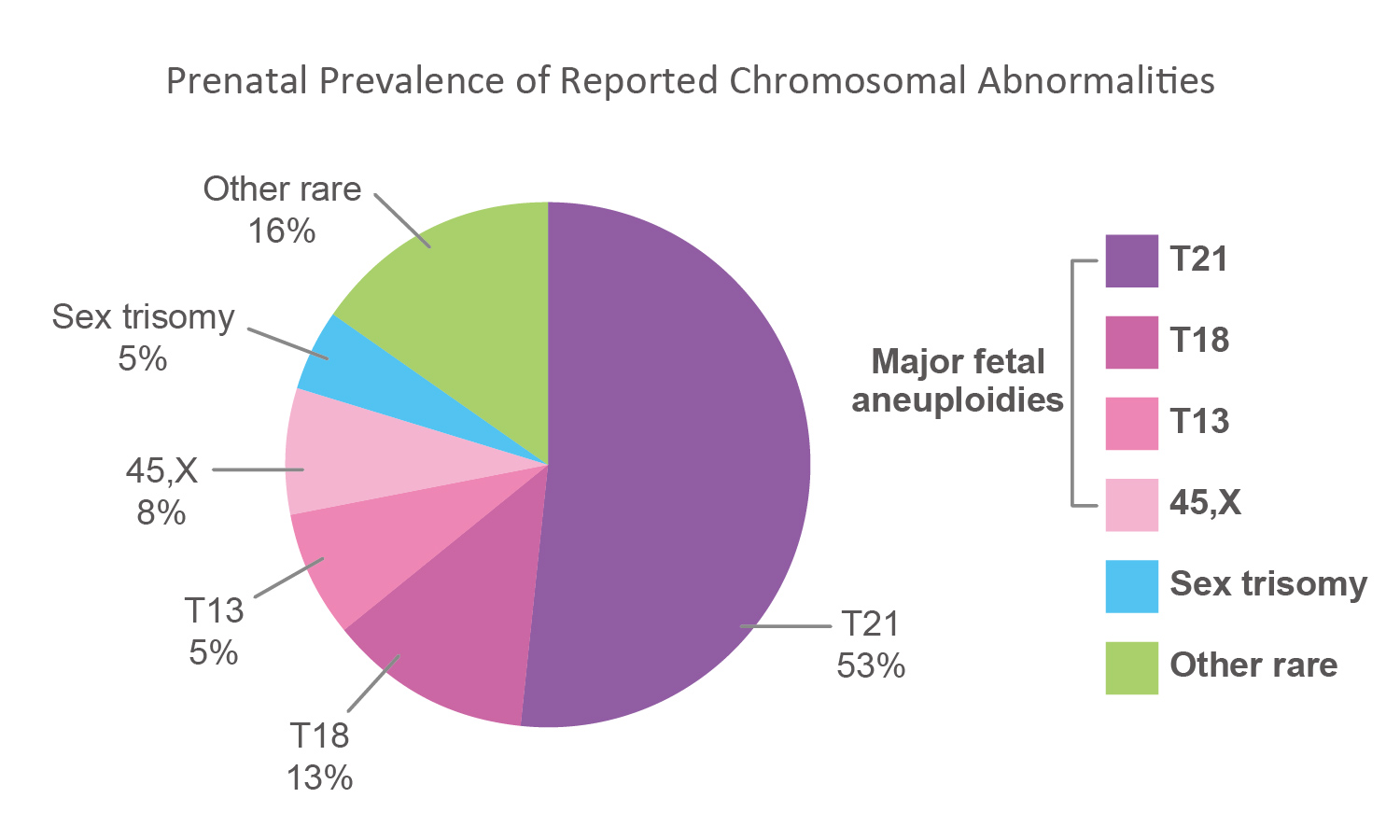
Although chromosome abnormalities in newborns typically involve the 13th, 18th and 21st chromosomes, there remains a 29% chance that the pregnancy is affected by other genetic diseases, particularly those which involve abnormalities in sex chromosomes or microdeletions. Targeted Sequencing and SNP based Targeted Sequencing are not able to identify these problems.
A company with experienced technicians can perform Genome-Wide Sequencing and thus achieve lower failure rates than those associated with Targeted Sequencing and SNP based Targeted Sequencing. Furthermore, Genome-Wide Sequencing can also check for microdeletions and assess the 23rd chromosome, thereby providing mothers with a more comprehensive understanding of their baby’s health.